Tuesday, April 27, 2010
FOR ANY QUERRY REGARDING BIOMEDICAL PROJECTS
Tuesday, April 13, 2010
BIOTECHNOLOGY LABS FOR MAKING PROJECTS
There are various fields and durations that you can opt depending on your university curriculum in doing a Project Work under Biotechnology at NTHRYS BIOTECH LABS.
Here you can download a detailed information sheet regarding durations and detailed fee structures mentioned for all fields in it.
http://www.nthrys.com/biotech_labs/nthrys_biotech_student_project_info.pdf If you cannot open or download the above pdf file use this link to see the same information from website.
http://www.nthrys.com/biotech_labs/nthrys_biotech_student_lab_projects.htmlIn the above information you can also see the reductions in the fee structures, if you are joining as a group.
You can select your duration with corresponding group choice [If you have a group] and you can follow the procedures given in the same sheet to apply for the project.
You can register the slot with the procedure given in the sheet.
The registration fee of Rs850/- which is charged to you is not an additional one.
It will be deducted from your main fee during the time of joining.
Feel free to mail us to counselor@nthrys.com or contact us on 9849854748 â€" Hyderabad â€" Andhra Pradesh for any queries or doubts.
Please visit our website www.nthrys.com
 for all our services.
for all our services.E-mail: coordinaot@nthrys.com
Telephone: 9849854748
Website: http://www.nthrys.com/biotech_labs/nthrys_biotech_student_project_info.pdf

Monday, April 12, 2010
Study Shows Significant Advantages of Computer-Assisted Robotic Total Knee Replacement
The key factor in successful total knee replacement is precise placement of the artificial joint so that the center of the patient’s hip and knee lines up within three degrees of the patient’s ankle. Using conventional techniques, the best surgeons achieve alignment within three degrees 50 to 80 percent of the time. At Mercy Medical Center, alignment within three degrees was achieved in all (100%) of the 1,000 computer-assisted robotic procedures performed between February, 2005 and January, 2010. Final post-surgical alignment averaged just under one degree (0.8).

Typically, the failure rate for knee replacements is three to eight percent per year, and one half of early knee replacement failures, those occurring less than two years after surgery, are attributed to misalignment, instability and aseptic loosening. These typically require a second more difficult and often less successful operation called a revision total knee replacement.
At Mercy Medical Center, there were no early failures and no revision operations secondary to misalignment, instability or aseptic loosening in the first 1,000 consecutive computer-assisted robotic total knee replacement patients over the first five years of the study.
Jan Koenig, MD, Director of Orthopedic Surgery at Mercy Medical Center, presented the findings on March 10, 2010 to a group of over 200 international orthopedic surgeons at the Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) in New Orleans. His presentation, The Evolution of Computer-Assisted Total Knee Replacement (CAS-TKR) Past, Present and Future, was a featured part of Medacta Orthopedics Scientific presentations.
It is estimated that as many as 500,000 total knee replacement surgeries currently are performed in the United States each year, with that number projected to increase to more than 4 million annually as the population ages.
Online Examination - Computer/IT Project
By virtue of today's socioeconomic environment and continuing advancements in information technologies, companies are offering more computer related services and becoming more sophisticated computers having high capacity of storage and fast method of retrieving real time information have become boon for corporate.Going on is an era of simplifying almost all complicated works using computers. Here, the external electrical/electronics device integration with computers has got a considerable importance. Here presents one of such projects Exam Online.
Existing System
The existing system has many problems to run this application. First of all the memory is not enough for a .net application. Then there is no apt compact device.
because in this project compact device is the client part, it can access inferno and it possess enough memory. The use of service with this available system is not easy.
Proposed System
The main aim of the proposed system is to overcome all the drawback of the existing system. The memory of the system is upgraded. In order to accomplish socket programming the status and configuration of the server side is increased. When we use the feature 'web reference' which is a main feature of .net we can easily access web service, it provides the facility of proxy. Also in this project the database used is SQL SERVER 2000 which is highly compatible Windows.
During evaluation and synthesis activity, the analyst create a model of the system to get a better understanding of data and control flow, functional processing, operational behaviour and information contents. The model serves as a foundation for the software design and basis for creation of specifications for software. At the core of the model is the data dictionary -a repository that contains description o1 data objects consumed or produced by the software.
REFERENCES
Network Monitoring System Communication
Network Monitoring System enables the local administrator to perform real time monitoring, data acquisition, data analysis and transmission .Here the administrator's work is made easier and simple.
Administrator is having options for new user registration, updating and deleting user accounts, enable or disable user accounts, time allotment of users, he can view the system details of any user, he can view the hardware and software defects in any system connected through the network, he can capture the system of any user using his system, detect failure in network and can access the full control of any user at any time, he can shutdown and reboot any system, chatting, and some other facilities in this system.
Whenever the administrator finds that a particular user performs an illegal activity, he can disable that user's account and the user is not permitted to log into the system.
The Administrator has some other options to view some details regarding the accounts and the registered users in the network. He can view the complaints, requests and feedback made by the users. He can view the logged users details such as current logic time, last logos time etc., time allotment list of all the users, system details of a particular user in the network etc..Only the registered user can use the service provided by flee System.
The services offered to the user are mailing, chatting, call services such as complain. request and feedback submission, and change password and view user's account details. Security features are also enhanced in the software by checking the user name, password and category. Time allotment for the user is done based on the user id. This system consists of mainly four modules namely failure detection, system details, user details and remote section.
Project Description
The main objective of this project is to develop a full fledged system giving detailed information about local network of a Campus. This project s focused mainly in administrative task.This software enables the local network administrator to view the entire network structure, to perform client control and real time monitoring, to find LAN traffic and failure detection and he can chat with the clients and check the complaints registered by them. The administrator can also change his password for ensuring security in the network.
Here the administrator monitors all the machines in the network and he has the facility to view the system configuration. He also monitor all the users logged on to the network and has the facility to , view the details of the users such as username, last logo OFF time, last login time, login date and privilege.
Administrator can perform real time monitoring by viewing the current connected machines in the network and logged in users and hence can find their processor, application and memory details. Administrator has the facility to know actual network structure, desktop capture, shutdown, restart and LogOFF a remote system from his system.
Administrator can defect the traffic i.e. the frequency, delay and bandwidth of the network cable laid and hence he could take a decision whether to replace network cables of higher bandwidth and thereby get the speed of data transfer increased. Security features are also included to the software by checking username and password.
Administrator can send online messages to all remote systems in the network or send online messages to a particular users logged into remote system. Call registration facility is provided for the users to register his complaints and requests. Administrator has the facility to view the complaint registered by the user and send a reply back to the user. The users can also send feedback about the resources provided by tile organization. Administrator can find the software installed in a machine.
Sunday, April 11, 2010
PROGRAM FOR SERIAL PORT COMMUNICATION WITH 8051
This program will read a complete line coming through my COM port in 8051.
This is the subroutine or function in c for accept line from serial port
void get_line(void)
{
char c, index=0;
while(c = getchar() != '\n')
{
buffer[index++] = c;
}
}
The main program
void main()
{
PCON = 0x80; // Double Baud Rate
SCON = 0x50; // SCON: mode 1, 8-bit UART, enable rcvr
TMOD |= 0x20; // TMOD: timer 1, mode 2, 8-bit reload
TH1 = BAUD_CONST; // TH1: reload value for desired baud. Calculate this for your crystal frequency
TR1 = 1; // TR1: timer 1 run
TI = 1;
RI = 0;
get_line(); //function call
}
REFERENCE BOOKS
Tab Electronics Guide to Understanding Electricity and Electronics
Publisher: McGraw-Hill | Pages: 459 | 2000-07-21 | ISBN 0071360573 | PDF | 3 MB
BOOK DESCRIPTION
Randy Slone's learn-as-you-go guide tells you how to put together a low-cost workbench and start a parts and materials inventory--including money-saving how-to's for salvaging components and buying from surplus dealers. You get plain-English explanations of electronic components-resistors, potentiometers, rheostats, and resistive characteristics-voltage, current, resistance, ac and dc, conductance, power...the laws of electricity...soldering and desoldering procedures...transistors...special-purpose diodes and optoelectronic devices...linear electronic circuits...batteries...integrated circuits...digital electronics...computers...radio and television...and much, much more. You'll also find 25 complete projects that enhance your electricity/electronics mastery, including 15 new to this edition, and appendices packed with commonly used equations, symbols, and supply sources.
Electronics Projects For Dummies
For Dummies | 2006 | ISBN: 0470009683 | 408 pages | PDF | 12,7 MB
Make lights dance to music, play with radio remote control, or build your own metal detector
Who says the Science Fair has to end? If you love building gadgets, this book belongs on your radar. Here are complete directions for building ten cool creations that involve light, sound, or vibrations -- a weird microphone, remote control gizmos, talking toys, and more, with full parts and tools lists, safety guidelines, and wiring schematics.
Check out ten cool electronics projects, including
* Chapter 8 -- Surfing the Radio Waves (how to make your own radio)
* Chapter 9 -- Scary Pumpkins (crazy Halloween decorations that have sound, light, and movement)
* Chapter 12 -- Hitting Paydirt with an Electronic Metal Detector (a project that can pay for itself)
Discover how to
* Handle electronic components safely
* Read a circuit diagram
* Troubleshoot circuits with a multimeter
* Build light-activated gadgets
* Set up a motion detector
* Transform electromagnetic waves into sound
Saturday, April 10, 2010
Bionic Eye Attempts to Restore Vision
A bionic eye prototype developed by researchers in Australia aims to implant an array of electrodes in the eye that can deliver electrical impulses directly to neurons in the retina.
The group, called Bionic Vision Australia, has developed a device called the wide-view neurostimulator for patients suffering from degenerative vision loss.
“It is really designed to give people back their mobility so they can move around their environment and avoid obstacles,” says Anthony Burkitt, research director of Bionic Vision Australia. “We are also working on a second-generation product that will help people recognize faces and read large print.”
Researchers worldwide are trying to find ways to use electronics to improve visual recognition. Last year, MIT announced it had developed a chip implant that could restore vision in some patients. MIT’s eyeball design holds a microchip that connects to an external coil on a pair of glasses. The chip receives visual information and activates electrodes that, in turn, fire the nerve cells that carry visual input to the brain.
Burkitt says other groups in Germany and Japan are working on similar projects. The difference largely lies in the the number of electrodes used, the configuration of the electrodes and how the data is transmitted.
Bionic Vision Australia uses an external camera — with resolution of up to 5 megapixels — mounted on a pair of glasses. An electrode array is implanted in the eye and that connects to the central part of the retina where the greatest number of retinal neurons are present. An external unit has vision-processing software to help generate the electrical impulses. The communication between the electrode implant and the external unit is wireless.
“The camera itself doesn’t need to be very powerful because the quality of the image isn’t the crucial component,” says Burkitt. “What’s important is the vision-processing software that picks up the image and transforms it into electrical impulses.”
The resultant vision is not the same as the images that a sighted person sees. Instead it’s a pixelated version with a relatively small number of dots: about 100 in early versions. But it’s a beginning, says Burkitt. Meanwhile, the team is also working on the next version of the bionic eye that will include 1,000 electrodes, delivering 10 times the resolution. It will be made of platinum, instead of the polycrystalline diamond used for the first one, so more electrodes can be packed in and better images generated.
Burkitt and his team hope to do the first human implant in 2013.
Friday, April 9, 2010
DELAY TIMER PROJECT-BASIC ELECTRONICS
In this Delay Timer project, all analog parts are being used with the thyristor as a device that switches an AC Relay ON or OFF depending on the timing of the RC circuit. The input mains supply used ranges from 220VAC to 240VAC and an AC relay (220-240VAC) is used to switch a load. The load to be switched must be within the current and relay ratings. This circuit is useful for use of devices that need to be OFF for a minimum of 150 - 210 secs after a mains supply have cuts off. Devices such as compressors and halagon lamp cannot be OFF and ON repeatedly within a short period of time as it will cause damage to the devices.
The use of microcontroller based devices are not reliable in that if the power supply cuts off and came back again in a short period of time, it will reset and "forgotten" its previous state. The use of RC circuitry as a timer circuit is reliable and is not susceptible to "memory loss" as in the case of microcontroller.
If a microcontroller based solution is used, extra circuitry such as backup battery or supercapacitor need to be incorporated in order to retain the memory of the MCU and to ensure that the clock still runs even after the supply has cuts off.
This project should be handled by experienced electronics designer as its part are powered on directly from the mains supply. As all parts is "live", one may get electric shock if care is not taken when testing the circuit. Some parts may "burst" if there are some short circuit in the circuit. It is not recommended to use breadboard to test the circuit. Circuit should be tested using printed circuit board and an isolating variable transformer where the voltage is slowly ramped up from zero.
Once tested working, the components should be potted using epoxy with only the terminals exposed. All parts are potted to prevent users from touching the parts.
google_protectAndRun("ads_core.google_render_ad", google_handleError, google_rend
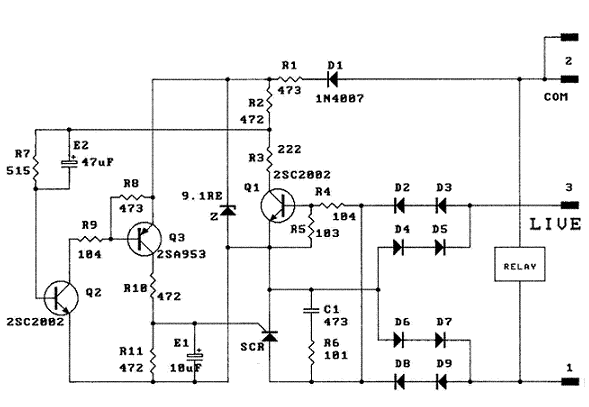
Schematic Diagram
The schematic below shows the circuit diagram of the ON delay timer. Once the mains power supply cuts off, the relay will only be able to turn ON after a period of 150 - 210 secs depending on the tolerance of the RC circuit represented by resistor R7(5.1 Mohm) and electrolytic capacitor E2(47uF). More accurate timing can be achieved by using low tolerance resistor and capacitor.
The thyristor used can be either 2P6M or MCR106-8 or equivalent parts available in the market. Relays used should have coil ratings below 1A in order not to overheat the SCR. No heatsink is required for the SCR.
At power on, there is no charge at E2, hence the transistor Q2 will be forward bias and turn ON when Q3 turn ON. Once these two transitors are ON, the SCR will turn ON as well. The use of C1 and R6 across the SCR acts as a snubber circuit to reduce the switching noise generated by the SCR when it turns OFF/ON. During the ON stage of the SCR, the capacitor E2 is charged to its maximum value. When the mains supply cuts off, the charge at capacitor E2 will cause the base of transistor Q2 to be reverse bias and cannot turn ON until almost all the charges have been discharged through resistor R7. Once the charge has been discharged (which will take around 150 - 210 secs for the values shown), transistor Q2 will be able to turn ON.
The timing of the circuit can be changed by reducing or increasing the RC values of R7 and E2.
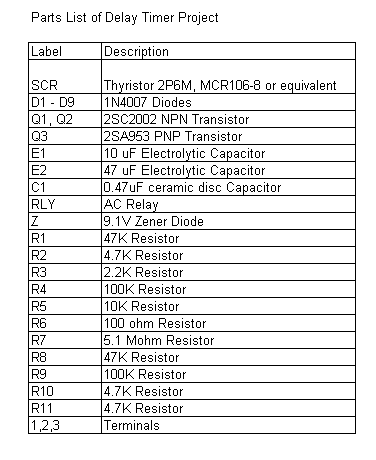
Parts List The parts list of the delay timer circuit is as shown below.
Wednesday, April 7, 2010
COMPUTER - IT PROJECT :- CREATE WEBSITE ON ONLINE NATIONAL POLLING
We live in a democracy and voting is one of our fundamental duties as responsible citizens of the country, but nowhere around the country a 100% people come to vote during the elections in their territory. There have been many reasons for that some of them are:
• In the rural areas the influential people keep their men at the polling booths to threaten the common man to vote for them
• There are many portions of the country like the North East where there is locally sponsored terrorism, at such places the security conditions are also not very bright, so naturally people feel afraid to come out of their houses and go to vote
• Net savvy new generation want hassle free voting system. Also the people in metros want a system through which they can vote for their territory without traveling.
Keeping in mind these situations and to improve the state of democracy in the country Online Polling System can be thought as a solution, in conjunction with the ongoing current manual voting system.
User of the System
A. General Public
B. Candidates
C. Administrators (Election Commission Officers)
D. Field Officers
Functional Requirements
i. Online registration for the voter id card which will be verified by the field officers (address and identity validation) and after receiving the field officer's report only the registration will be validated and a voter id will be issued (a photograph will have to be uploaded). You can also think about any other secure method like digital signature.
ii. Those already having a voter id card can register for the online voting system, they will use their voter id as their user name and a separate password will be used for secure authentication.
iii. The election commission will be able to use the site to let the candidates register for their nomination on the site and their officers will validate it. Candidates can run their election campaign through forums and chat-room.
iv. A detailed profile of all the candidates constituency wise will be maintained so that voters can always know about the candidates of their area.
v. Once registered when ever polling is done in any area that areas' people will be able to vote for their favorite candidates.
vi. Devise a mechanism that ensures duplicates voting (online & offline) is not happening.
vii. The system would show the current statistics as well on the web site about how many votes which candidates have got.
viii. Later when the voting ends the administrator can add the manual poling results to the database to calculate the final results which will immediately be flashed on the site.
ix. Facilitate appropriate communication between all stakeholders - Discussion forum/chat/mail/polls
x. Candidates should be able to modify selected portions of their profile after registration for nomination like the promises they make about the things to do after winning the election, their previous works, their experiences and a comprehensive about me, etc.
Optional Features
1. Java based client for User-C & D
2. SMS based inquiry of the voting results
3. Customizable color skins.
DEVELOPMENT OF AN AUTO-SUMMARIZATION TOOL -- IT PROJECT
This has some applications like summarizing the search-engine results, providing briefs of big documents that do not have an abstract etc. There are two categories of summarizers, linguistic and statistical. Linguistic summarizers use knowledge about the language to summarize a document. Statistical ones operate by finding the important sentences using statistical methods. Statistical summarizers normally do not use any linguistic information.
User of the System
Used to generate summaries of electronic documents
Using statistical techniques
To handle the document types like Plain Text, HTML, Word Document
Techniques involve finding the frequency of words, scoring the sentences, ranking the sentences
Functional Requirements
i. Study about auto-summarizing techniques & concentrate more on summarizers based on statistical techniques
ii. Collect the list of stop-words from an Internet site
iii. Come up with algorithms for the different functional components listed in the previous section. Some heuristic methods could be used to come up with modification of any existing algorithm
iv. Implement the pre-processor/sentence separator/word separator/word frequency calculator. These do not require much work on the algorithm side and existing algorithms will do fine.
v. Implement the scoring and ranking component
vi. Test it with some documents and tune the algorithms, if needed
vii. Bench-mark your tool against some tools available on the Internet
Optional Features
This algorithm determines the score of each sentence. Several possibilities exist. The score can be made to be proportional to the sum of frequencies of the different words comprising the sentence The score can also be made to be inversely proportional to the number of sentences in which the words in the sentence appear in the document. Likewise, many such heuristic rules can be applied to score the sentences.
The sentences will be ranked according to the scores. Any other criteria like the position of a sentence in the document can be used to control the ranking. For example, even though the scores are high, we would not put consecutive sentences together
Based on the user input on the size of the summary, the sentences will be picked from the ranked list and concatenated. The resulting summary file could be stored with a name like
Other Important issues
After finalizing on the algorithms, the system is integrated so that it is possible to test using a GUI or a command line interface
The tool should be tested with documents of different size and content
Tuesday, April 6, 2010
Electronic Timer Switch - TIMER PROJECTS
Schematic Diagram
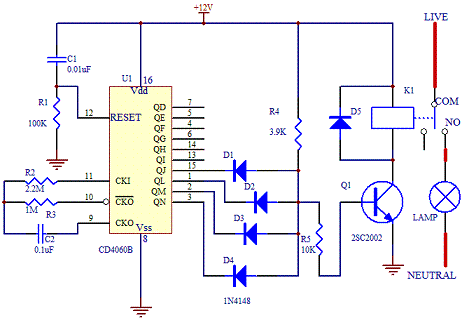
The core of this electronic timer switch project uses a CD4060B binary counter. The binary counter has 10 outputs and the counter are counted by configuring the oscillator. Every negative clock will trigger the counter of the IC internally.
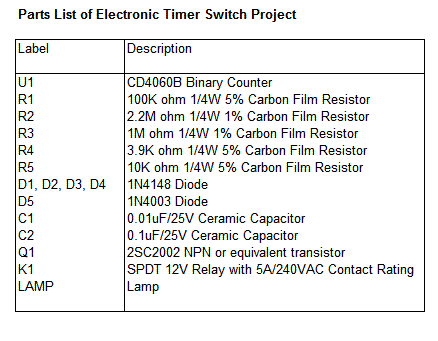
Parts List
Monday, April 5, 2010
DC motor speed control
Sunday, April 4, 2010
BASIC ELECTRONICS-TIMER CIRCUIT DESIGN
Timer circuit has been used in many projects and there are basically 2 types that are used these days. One of them is the use of analog RC circuit where charging of the capacitor circuit determined the T(time) of the circuitry. This type of circuitry has larger tolerance and is used in applications where the T is not so critical as the T is affected by the tolerance of the RC components used.
The other is the use of crystal or ceramic resonators together with microprocessor, microcontroller or application specific integrated circuit that need higher precision T in the tolerance of up to 5 ppm (parts per million).
555 IC
One commonly used circuit is the 555 IC which is a highly stable controller capable of producing timing pulses. With a monostable operation, the T(time) delay is controlled by one external resistor and one capacitor. With an astable operation, the frequency and duty cycle are accurately controlled by two external resistors and one capacitor. The application of this integrated circuit is in the areas of PRECISION TIMING, PULSE GENERATION, TIMING DELAY GENERATION and SEQUENTIAL TIMING.
A typical 555 IC block diagram is as shown below.
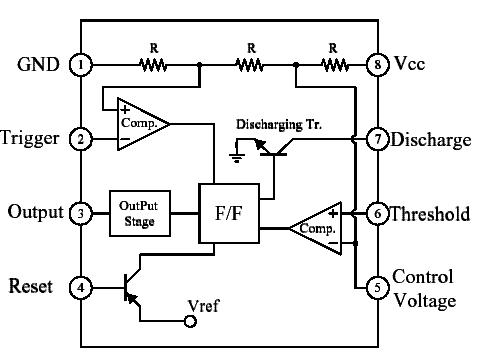
Monostable Operation
Figure below shows the monostable operation of a 555 IC.

In this mode, the device generates a fixed pulse whenever the trigger voltage falls below Vcc/3. When the trigger pulse voltage applied to pin 2 falls below Vcc/3 while the its output is low, its internal flip-flop turns the discharging transistor Tr off and causes the output to become high by charging the external capacitor C1 and setting the flip-flop output at the same instant. The voltage across the external capacitor C1, VC1 increases exponentially with the time constant T=RA*C1 and reaches 2Vcc/3 at td=1.1RA*C1. Hence, capacitor C1 is charged through resistor RA. The greater the time constant RA*C1, the longer it takes for the VC1 to reach 2Vcc/3. In other words, the time constant RA*C1 controls the output pulse width. When the applied voltage to the capacitor C1 reaches 2Vcc/3, the comparator on the trigger terminal resets the flip-flop, turning the discharging transistor Tr on. At this time, C1 begins to discharge and its output goes to low.
Astable Operation

An astable operation is achieved by configuring the circuit as shown above. In the astable operation, the trigger terminal and the threshold terminal are connected so that a self-trigger is formed, operating as a multivibrator. When its output is high, its internal discharging transistor Tr turns off and the VC1 increases by exponential function with the time constant (RA+RB)*C. When the VC1, or the threshold voltage, reaches 2Vcc/3, the comparator output on the trigger terminal becomes high, resetting the F/F and causing its output to become low. This in turn turns on the discharging transistor Tr and the C1 discharges through the discharging channel formed by RB and the discharging transistor Tr. When the VC1 falls below Vcc/3, the comparator output on the trigger terminal becomes high and the timer output becomes high again. The discharging transistor Tr turns off and the VC1 rises again. The frequency of oscillation is given as below.

AUDIO WATTMETER

Parts List For An Audio Wattmeter
BP1, BP2 – Insulated binding posts
C1, C2 – 100 uF, 50 VDC
D1, D2, D3, D4 – Diode, HEP-134
M1 – 0.1 mA DC Meter
R1 – 8 ohm, 100 watt resistor, see text
R2 – 1500 ohm linear taper potentiometer
LOAD MATCHER

A minimum loss pad is the device used to match a high impedance to a low impedance. Though there is always a signal level loss through a pad, the circuit shown provides the absolute minimum loss that can be obtained while providing a precise match. If the resistance values work out to odd values, such as 134 ohms, use the closest standard value. Though 5 percent tolerance resistors are suggested, almost as good performance will be obtained with 10 percent resistors.
REMOTE SPEAKER SETUP

Switch S1 turns the remote speaker on and off. Since transistor amplifiers usually put out more power at 4 ohms than at 8 or 16 ohms, adding the extra speakers does not substantially reduce the volume at the main speakers because the amplifier sees a lower impedance load and attempts to drive more power output into the combined speaker load. If your speakers are 4 ohms, and you plan to use 4 ohm remote speakers use the circuit modification shown. Switching in the remote speaker will result in the main and remote speakers being series connected for a total load of 8 ohms.
MUSCULAR BIO STIMULATOR
Working Of The Circuit
IC1 generates 150µSec. pulses at about 80Hz frequency. Q1 acts as a buffer and Q2 inverts the polarity of the pulses and drives the Transformer. The amplitude of the output pulses is set by P1 and approximately displayed by the brightness of LED D1. D2 protects Q2 against high voltage peaks generated by T1 inductance during switching.

Components Used
P1______________4K7 Linear Potentiometer
R1____________180K 1/4W Resistor
R2______________1K8 1/4W Resistor (see Notes)
R3______________2K2 1/4W Resistor
R4____________100R 1/4W ResistorC1____________100nF 63V Polyester Capacitor
C2____________100µF 25V Electrolytic CapacitorD1______________LED Red 5mm.
D2___________1N4007 1000V 1A DiodeQ1,Q2_________BC327 45V 800mA PNP Transistors
IC1____________7555 or TS555CN CMos Timer IC
T1_____________220V Primary, 12V Secondary 1.2VA Mains Transformer
SW1____________SPST Switch (Ganged with P1)
B1_____________3V Battery (two 1.5V AA or AAA cells in series etc.)
Notes
T1 is a small mains transformer 220 to 12V @ 100 or 150mA. It must be reverse connected i.e. the 12V secondary winding across Q2 Collector and negative ground, and the 220V primary winding to output electrodes.
Output voltage is about 60V positive and 150V negative but output current is so small that there is no electric-shock danger.
In any case P1 should be operated by the “patient”, starting with the knob fully counter-clockwise, then rotating it slowly clockwise until the LED starts to illuminate. Stop rotating the knob when a light itch sensation is perceived.
Best knob position is usually near the center of its range.
In some cases a greater pulse duration can be more effective in cellulite treatment. Try changing R2 to 5K6 or 10K maximum: stronger pulses will be easily perceived and the LED will shine more brightly.
Electrodes can be obtained by small metal plates connected to the output of the circuit via usual electric wire and can be taped to the skin. In some cases, moistening them with little water has proven useful.
SW1 should be ganged to P1 to avoid abrupt voltage peaks on the “patient’s” body at switch-on, but a stand alone SPST switch will work quite well, provided you remember to set P1 knob fully counter-clockwise at switch-on.
Current drawing of this circuit is about 1mA @ 3V DC .
Some commercial sets have four, six or eight output electrodes.
To obtain this you can retain the part of the circuit comprising IC1, R1, R2, C1, C2, SW1 and B1.
Other parts in the diagram (i.e. P1, R3, R4, D1, D2, Q2 & T1) can be doubled, trebled or quadrupled.
Added potentiometers and R3 series resistors must be wired in parallel and all connected across Emitter of Q1 and positive supply.
Commercial sets have frequently a built-in 30 minutes timer. For this purpose you can use the Timed Beeper.
HOW TO MAKE A TAN TIMER
A Rotary Switch sets the timer according to six classified Photo-types (see table).
A Photo resistor extends the preset time value according to sunlight brightness (see table).
When preset time ends, the beeper emits an intermittent signal and, to stop it, a complete switch-off of the circuit via SW2 is necessary.
| Photo-type | Features | Exposure time |
| I & children | Light-eyed, red-haired, light complexion, freckly | 20 to 33 minutes |
| II | Light-eyed, fair-haired, light complexion | 28 to 47 minutes |
| III | Light or brown-eyed, fair or brown-haired, light or slightly dark complexion | 40 to 67 minutes |
| IV | Dark-eyed, brown-haired, dark complexion | 52 to 87 minutes |
| V | Dark-eyed, dark-haired, olive complexion | 88 to 147 minutes |
| VI | The darkest of all | 136 to 227 minutes |
| Note that pregnant women belong to Photo-type I | ||

Components Used
R1_____________47K 1/4W Resistor
R2______________1M 1/4W Resistor
R3,R5_________120K 1/4W Resistors
R4____________Photo resistor (any type)
C1,C3__________10µF 25V Electrolytic Capacitors
C2____________220nF 63V Polyester Capacitor
D1,D2________1N4148 75V 150mA Diodes
IC1____________4060 14 stage ripple counter and oscillator IC
IC2____________4017 Decade counter with 10 decoded outputs IC
Q1____________BC337 45V 800mA NPN Transistor
SW1___________2 poles 6 ways Rotary Switch (see notes)
SW2___________SPST Slider Switch
BZ1___________Piezo sounder (incorporating 3KHz oscillator)
B1____________3V Battery (two 1.5V AA or AAA cells in series etc.)
NOTES
- Needing only one time set suitable for your own skin type, the rotary switch can be replaced by hard-wired links.
- A DIP-Switch can be used in place of the rotary type. Please pay attention to use only one switch at a time when the device is off, or the ICs could be damaged.
Electronic Sleep Inducer
Features Of Sleep Inducer
* Generates a natural electromagnetic-field
* Makes easier to fall asleep
* Induces a prolonged and sound sleep without drugs
* No side effects

How To Use The Circuit
Select a timing option by means of the rotary switch SW1.
Choose 15, 30 or 60 minutes operation.
Select “Stop” or “Alternate” mode operation by means of SW2.
With SW2 closed (Stop mode operation) the electromagnetic radiation stops after the pre-set time is elapsed.
With SW2 opened (Alternate mode operation) the device operates for the pre-set time, then pauses for the same amount of time: this cycle repeats indefinitely.
Place the unit under the pillow and sleep like a log.
To reset a cycle press P1 push button.
IC2C and IC2D generate two square waves at about 1.2 and 5 Hz respectively. These wave-forms are converted into 60µS pulses at the same frequencies by means of C5 & C6 and mixed at Q1 Base. This transistor drives the Radiator coil with a scalar series of pulses of 60µS length and 9V amplitude.
IC1, IC2A & IC2B form the timer section. C1 & R2 provide auto-reset of IC1 at switch-on. The internal oscillator of IC1 drives the 14 stage ripple counter and, after about 15 minutes, output pin 1 goes high. Pin 3 of IC2A goes low and stops IC2C & IC2D oscillation.
If SW2 is left open (Alternate mode operation), after 15 minutes pin 1 of IC1 goes low, pin 3 of IC2A goes high and oscillators are enabled again.
If SW2 is closed (Stop mode operation), the first time output pin 1 of IC1 goes high, the internal oscillator of the IC is disabled by means of D1. Therefore the circuit remains off until a reset pulse is applied to pin 12 by means of P1 or when the whole device is switched-off and then restarted.
The same thing occurs when SW1 is switched on 30 or 60 minutes positions, obviously changing time length.
IC2B drives pilot LED D2 which operates in the following three modes:
Flashes quickly and almost randomly when the Radiator coil is driven
Flashes somewhat slowly and regularly when the Radiator coil is pausing during the Alternate mode operation
Is off when the circuit auto-stops (Stop mode operation)
Components Used
R1,R5___________1K 1/4W Resistors
R2_____________10K 1/4W Resistor
R3,R6__________10M 1/4W Resistors
R4,R7___________2M2 1/4W Resistors
R8,R9___________4K7 1/4W Resistors
C1,C7__________47µF 25V Electrolytic Capacitors
C2____________100nF 63V Polyester Capacitor
C3,C4_________330nF 63V Polyester Capacitors
C5,C6__________15nF 63V Polyester Capacitors
D1,D3,D4,D5__1N4148 75V 150mA Diodes
D2______________LED (any type) (see Notes)
IC1____________4060 14 stage ripple counter and oscillator IC
IC2____________4093 Quad 2 input Schmitt NAND Gate IC
Q1____________BC327 45V 800mA PNP Transistor
L1____________Radiator coil (see Notes)
P1____________SPST Pushbutton
SW1___________2 poles 4 ways rotary switch
SW2___________SPST Slider Switch
B1____________9V PP3 Battery
Clip for PP3 Battery
Notes
L1 is obtained by winding randomly 600 turns of 0.2 mm. enameled wire on a 6 mm. diameter, 40 mm. long, steel bolt. Secure the winding with insulating tape.
Mean current drawing is about 7mA, decreasing to less than 4mA during pauses when in Alternate mode operation.
Battery life can be dramatically increased omitting LED D2 and its associated resistor R5.
Use a plastic box to enclose the circuit: metal cases can severely limit electromagnetic radiation.
HOW TO MAKE FM TUNING METER
Those inexpensive portable Public Service Radios do a fine job of receiving police and fire calls. But if you are not tuned precisely to the center channel of the base station, it’s more than likely you don’t hear the much weaker signals from the mobiles. With an FM Tuning Meter hooked onto your public service inhaler, you’ll be able to copy any signal that can fight it’s way into the antenna terminals. The schematic shows a detector circuit common to most public service portables. Resistor Rx and Capacitor Cx form the de-emphasis network. Connect one end of sensitivity control R1 to the junction of Rx and Cx as shown. Meter M1 is the zero center miniature type; one rated either 50 or 100 microamperes will be satisfactory. Adjust R1 so the meter pointer is not driven offscale when the signal is detuned to the extreme of the sidebands. Proper tuning is then indicated when the meter shows center scale.

Parts List For FM Tuning Meter
M1 – 50 or 100 microAmpere meter, zero center
R1 – 1 megohm miniature potentiometer
HOW TO MAKE - MIKE DESENSITIZER
Many cassette recorders do not have a high level (aux) input; they are meant only for use with microphones. If you try to dub directly from another recorder’s “line” output, or from across the speaker, the relatively high signal level overloads the microphone input, causing severe distortion. Good dubs can be obtained by attenuating the high level signal almost 50 dB, so the attenuated signal is essentially equal to microphone level. This recorder bridging cord provides about 50 dB attenuation in a single, easy-to-handle assembly. Connect resistor R1 in series with the shielded cable hot lead. Connect the free end of R1 to recorder plug PL2 and one end of resistor R2. Fold R2 back adjacent to R1 and solder the free end to the cable shield. Loop a wire from the shield to the PL2 outside (sleeve) terminal. PL1 should match the output jack of the recorder you dub from.

Part List For Mike Desensitizer
PL1, PL2 – Plugs to match existing tape equipment Shielded cable
R1 – 100,000 ohm, 1/4 – watt resistor
R2 - 10,000 ohm, 1/4 – resistor
STEREO SHUTOFF
It happens to just about everyone. One minute you’re listening to the hi-fi, the next you’re called away to answer the doorbell or a phone call. You forget all about the music, the record plays through, the automatic turntable shuts off — but the amplifier stays on until you happen to pass by and notice the glow from the pilot lamps. Yet, this simple circuit, which you can throw together in less than an hour, will automatically turn off the amplifier when the turntable shuts off. The relay coil voltage is taken from across the phonomotor; when the turntable motor is on, relay K1 closes and applies power to AC socket SO1; When the turntable shuts off, removing voltage from the motor, K1 opens, disconnecting power from outlet. Because the turntable automatic shutoff switch might not be able to carry the amplifier load, the AC power for SO1 is taken off before the automatic shutoff switch. Switch S1 bypasses the relay contacts and applies power to the socket even when the turntable is off.

Parts List For Stereo Shutoff
K1 – 117V AC relay with contacts rated at least 5 amperes at 117V AC (Radio Shack 275-207)
S1 – Switch, SPST (Shutoff bypass)
SO1 – AC Socket


![Reblog this post [with Zemanta]](http://img.zemanta.com/reblog_e.png?x-id=c55e82bb-a219-4dc2-8e2c-229368457530)
![Reblog this post [with Zemanta]](http://img.zemanta.com/reblog_e.png?x-id=75f7ae53-0c83-4e83-8347-d0b5a6d6c3b7)





